Stimulant medications, like Vyvanse®, are often the first line of treatment for adult ADHD and are effective for many people. However, recent shortages have caused some users to look for viable alternatives.
In addition to the stimulant shortage, there are many reasons to consider a nonstimulant alternative to Vyvanse. Stimulants have a risk of dependence and cause unwanted side effects in some users. For others, stimulants do not effectively treat their ADHD symptoms.
Stimulant or nonstimulant, it’s important to understand all the benefits, risks and side effects of medications. Learn more here in this comparison of stimulant Vyvanse with other commonly prescribed nonstimulant ADHD medications.
Key Takeaways
Vyvanse® is one of several prescription stimulant medications used to treat adult ADHD by improving focus and reducing impulsivity.
Nonstimulant options for adult ADHD include atomoxetine (Strattera®), viloxazine (Qelbree®) and certain blood pressure medications. These are often considered when people cannot tolerate stimulants, have side effects or have concerns about dependence.
Some people prefer nonstimulant medications because they generally have a lower risk of misuse and may be better suited for those with certain heart conditions or anxiety disorders.
A licensed provider can help you compare ADHD treatment options and choose the best plan based on your symptoms, health history and daily needs.
What is Vyvanse?

Vyvanse is the brand name of the medication lisdexamfetamine. It belongs to a class of medications called central nervous system (CNS) stimulants and works by adjusting the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, including dopamine and norepinephrine.1 Vyvanse is primarily prescribed to treat ADHD symptoms and binge eating disorder.2
In studies, Vyvanse was shown to start improving ADHD symptoms in adults at approximately two hours after taking a dose and the effects last up to 14 hours.3
Risks and side effects of Vyvanse
Vyvanse is a federally controlled substance that carries a risk of dependence.4 It’s important to take Vyvanse only as prescribed. Taking more than prescribed can increase the risk of dependence and cause unwanted, severe side effects.5
When taken as prescribed, common side effects of Vyvanse include:6
Sleepiness.
Dizziness.
Headache.
Dry mouth.
Constipation.
Diarrhea.
Nausea.
Weight loss.
Vyvanse Alternative Adult ADHD Medications

Vyvanse isn’t for everyone. There are alternative medications, stimulant and nonstimulant, available to treat adult ADHD.
Stimulant ADHD medications
Stimulants are the most prescribed medication to treat ADHD and work by increasing the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. These neurotransmitters play a role in attention and motivation.7 Stimulants are effective at managing ADHD symptoms in up to 75% of users.8
There are two main groups of stimulant medications for ADHD: amphetamines and methylphenidates.
Amphetamines prescribed for ADHD include lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse®), dexamphetamine (Dexedrine®) and mixed amphetamine salts (Adderall®). Amphetamines come with a risk of dependence and other side effects, including:9
Anxiety, irritability and behavioral problems.
Circulation problems.
Erectile dysfunction.
Heart disease.
Nausea.
Psychosis.
Severe fatigue or difficulty sleeping.
Swelling of blood vessels.
Methylphenidates prescribed for ADHD include Ritalin® and Concerta®. These drugs have a risk of dependence and common side effects, including:10
Fast heartbeat.
Chest pain.
Fever.
Joint pain.
Skin rash or hives.
Nonstimulant ADHD medications
While stimulant medications work for many people with ADHD, the side effects and risk of dependence have steered many toward nonstimulant medications. Nonstimulant ADHD medications can be classified into five categories:11

1. Tricyclic antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA) have the most evidence of effectively treating ADHD out of the nonstimulant medications, with 91% of adolescents and adults reporting improved symptoms. Imipramine (Tofranil®) and desipramine (Norpramin®) are the most studied types of TCAs. These drugs work by balancing neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain.12
Potential side effects of TCAs include:13
Constipation.
Dry mouth.
Dizziness.
Urinary retention.
Blurred vision.
Fast heartbeat.
Drops in blood pressure when standing up (orthostatic hypotension).
Increased appetite.
Weight gain.
2. Nontricyclic antidepressants.
Bupropion (Wellbutrin XL®), venlafaxine (Effexor®) and viloxazine (Qelbree®) are examples of nontricyclic antidepressants prescribed to treat ADHD. They work by increasing neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine. Bupropion is significantly effective at treating ADHD in clinical studies. Venlafaxine has had varying degrees of success rates in studies.14 Viloxazine has shown promising results for treating adult ADHD in studies.15
Potential side effects of bupropion include:16
Anxiety.
Body aches or pain.
Chills.
Cough.
Dry mouth.
Ear congestion.
Fever.
Hyperventilation.
Irregular heartbeats.
Irritability.
Loss of voice.
Restlessness.
Shaking.
Sneezing.
Sore throat.
Stuffy or runny nose.
Trouble breathing.
Trouble sleeping.
Unusual tiredness or weakness.
Potential side effects of venlafaxine include:17
Sexual dysfunction.
Lack or loss of strength.
Severe headache.
Sweating.
Common side effects of viloxazine include:18
Loss of appetite.
Tiredness.
Nausea.
Vomiting.
Headache.
3. Specific norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.
Atomoxetine (Strattera®) is a specific norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor that has shown promise in studies for treating ADHD. In some studies, atomoxetine was as effective as methylphenidate stimulant medications in reducing ADHD symptoms.19
Common side effects of atomoxetine include:20
Belching.
Change in periods or bleeding between periods.
Chest tightness.
Cough.
Decrease in the frequency or volume of urination.
Decreased appetite.
Constipation.
Dizziness.
Dry mouth.
Fever.
Headache.
Heartburn.
Irritability.
Loss in sexual ability, desire, drive or performance.
Nausea.
Painful urination.
Sleepiness or unusual drowsiness.
Stuffy or runny nose.
Trouble breathing.
Trouble sleeping.
Vomiting.
4. Alpha-2 noradrenergic agonists.
Two commonly prescribed nonstimulant ADHD medications are the alpha-2 nonandrogenic agonists guanfacine (Intuniv®) and clonidine (Kapvay®). Both have been shown to be effective at treating ADHD in clinical trials. However, research on safety and efficacy has been limited. Elevated blood pressure was a concern in studies.21
Common side effects of guanfacine include:22
Constipation.
Dizziness.
Dryness of the mouth.
Nausea.
Sleepiness or unusual drowsiness.
Unusual dullness or feeling of sluggishness.
Upper abdominal or stomach pain.
Weight gain.
Common side effects of clonidine include:23
Constipation.
Darkening of the skin.
Decreased sexual ability.
Dry, itchy or burning eyes.
Loss of appetite.
Nausea or vomiting.
5. Nonschedule stimulants.
Modafinil is a stimulant ADHD medication that is not classified by the FDA as a controlled substance. It was initially developed to be a treatment for narcolepsy and has shown some positive results in treating ADHD in research studies.24
Common side effects of modafinil include:25
Anxiety.
Headache.
Nausea.
Nervousness.

Convenient, affordable adult ADHD treatment on your schedule.
Your mental health is important. RedBox Rx offers secure, private online consultations with licensed providers focused on patient outcomes.
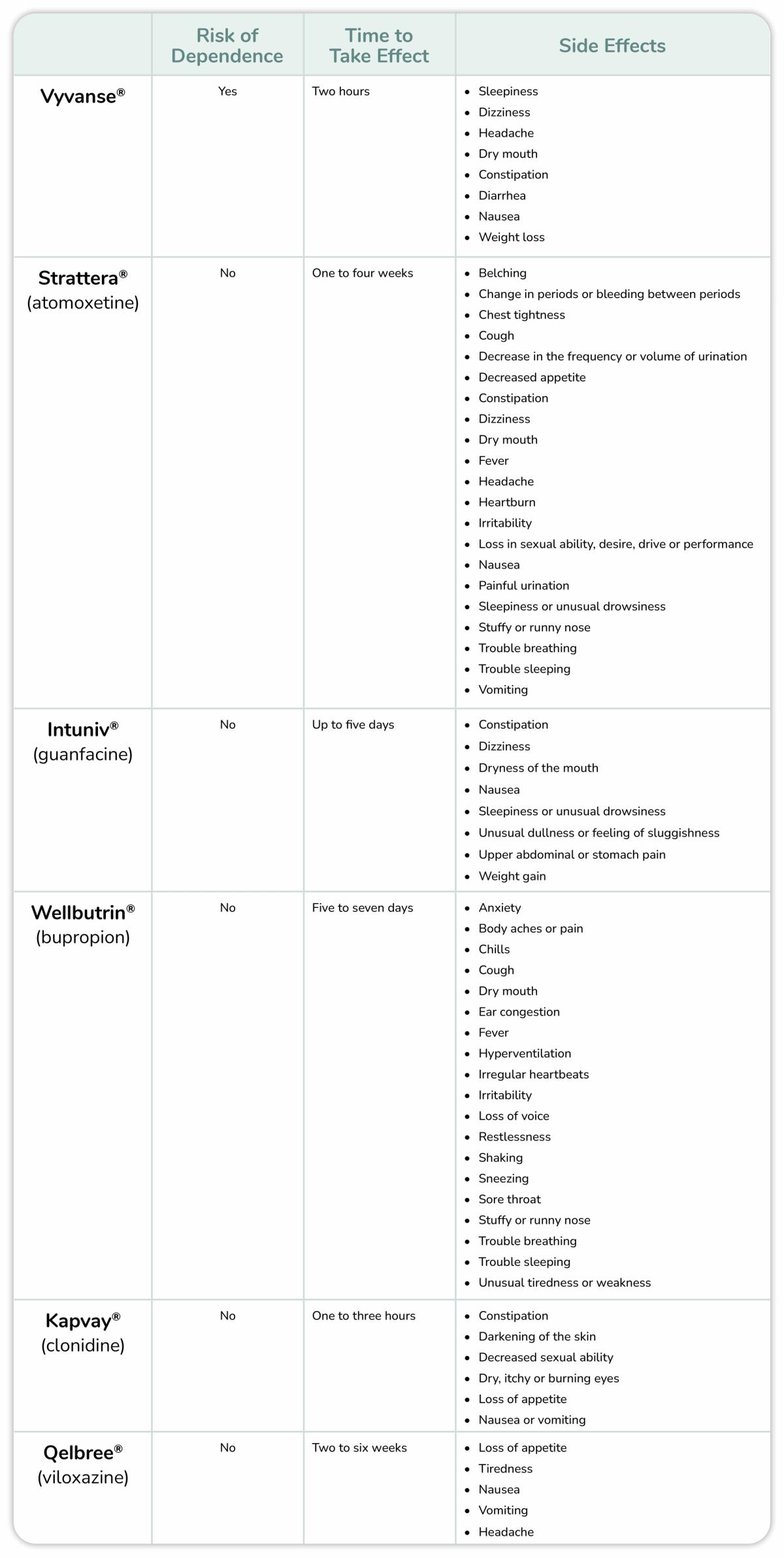
Get StartedVyvanse vs. Nonstimulant ADHD Medication Comparison
See how the stimulant Vyvanse compares to commonly prescribed nonstimulant medications for ADHD.
Vyvanse vs. Strattera® (atomoxetine)
Vyvanse and Strattera (atomoxetine) have both been clinically proven to improve symptoms of ADHD. In one study, participants reported significant improvements in ADHD symptoms. However, Vyvanse was reported to work quicker than Strattera in a nine-week trial.26 The average time to feel the full effects of Strattera is up to one month.27
The main difference between these two medications is the risks. Vyvanse is a controlled substance that carries a risk of dependence. There have also been reports of cardiac problems in users of Vyvanse.28
Vyvanse vs. Intuniv® (guanfacine)
Intuniv (guanfacine) and Vyvanse have both proven effective at treating ADHD. Stimulant medications like Vyvanse are faster acting than Intuniv, and it can take up to five days to see full results. Intuniv is better tolerated and most people who take this medication experience no side effects.29 Vyvanse carries a risk of dependence, more severe side effects and the potential for cardiac issues.30
Vyvanse vs. Wellbutrin® (bupropion)
According to research, stimulants like Vyvanse can be more effective than bupropion in treating ADHD. Vyvanse also acts quicker and takes effect within two hours.31 Bupropion can take five to seven days before results are realized.32
Vyvanse has a risk of dependence, while bupropion is not habit forming. Bupropion does carry a black box warning from the FDA that it can cause suicidal thoughts in users, particularly in young adults.33
Vyvanse vs. Kapvay® (clonidine)
In clinical trials, both Vyvanse and Kapvay showed significant improvements in ADHD symptoms. When paired together, they produced better results than using just one treatment at a time.34 While Kapvay isn’t habit forming like Vyvanse; it is recommended that a prescription be tapered off rather than stopped suddenly. Kapvay can cause sedation, which is not a side effect of Vyvanse.35
One advantage Kapvay has over other nonstimulants is that it is as fast acting or faster, than Vyvanse. Kapvay reaches peak concentrations within one to three hours.36 Vyvanse starts to work at around two hours.
Vyvanse vs. Qelbree® (viloxazine)
Qelbree does not carry a risk of dependence like Vyvanse. Qelbree does, however, have a history of suicidal ideation in some users that should be monitored.37 In a six-week study of Qelbree, participants reported a 41% reduction in ADHD symptoms. Some participants reported improvements as early as two weeks.38 Vyvanse can take effect as soon as two hours.
Vyvanse vs. Nonstimulant Adult ADHD Med Comparison Chart
How RedBox Rx can help

RedBox Rx makes receiving nonstimulant treatment for adult ADHD easy and affordable.
Benefits of RedBox Rx include:
Transparent, affordable, flat rates on medications starting at $25/month (with purchase of three-month supply).
$35 online consultations with a U.S. licensed medical professional.
No membership fees. No insurance required. FSA and HSA eligible.
Free shipping directly to you. Monthly and quarterly subscriptions available.
Start your treatment today with our online ADHD assessment.


